Workshop
| מערכת: | אתר הקורסים של הטכניון - תשפ"ה |
| קורס: | Training Site For Teachers |
| ספר: | Workshop |
| הודפס על-ידי: | משתמש אורח |
| תאריך: | יום שלישי, 4 נובמבר 2025, 4:43 AM |
תיאור
A "workshop" activity allows you to present a task or assignment that requires peer review and evaluation.
Introduction

Workshop is an effective teaching strategy based on student participation and engagement in the assessment process, particularly suited to achieving the goals of academic teaching in various content areas. Research indicates a good match between faculty grades and teacher assessments and student assessments. Therefore, student assessments can be used.
Workshop is a high-level thinking task that allows students to become familiar with the criteria used to evaluate their work, and contributes to students' advancement of understanding and professional skills. Research suggests that workshop is an effective strategy for enhancing the learning process and increasing motivation (Conway et al., 1993; Falchikov & Goldfinch, 2000).
The Moodle system enables the effective implementation of workshop in teaching, while maintaining anonymity, accessibility to peer work and assessment criteria, the possibility of online submission of the assessment, automatic processing of data and presentation of assessment results.
Workshop in the Moodle system
- In the workshop activity in Moodle, a student submits a work, and subsequently, evaluates several works submitted by peers.
- In the workshop activity, students receive two grades (1) a grade for submitting the work (2) a grade based on the assessments of their peers. Both grades are recorded in the course grade sheet.
The peer assessment activity includes five stages, and the lecturer moves the assignment from stage to stage, depending on progress:
Preparation: The lecturer defines the characteristics of the activity, the timetable and the indicator (this stage can also be returned to later). At this stage, an example of the assessment can be uploaded.
Submission: Students submit assignments, according to the lecturer's instructions.
The lecturer defines assignments for assessment by manual assignment or, alternatively, by automatic assignment.
Peer assessment: Students evaluate the work of their peers using a structured indicator (evaluation form), which contains evaluation criteria (indicators) defined by the lecturer.
Assessment and grading: The system automatically assigns grades consisting of the grade for the submitted work and a grade for the quality of the assessment.
Closing: The grades are transferred to the grade sheet in the Moodle system and each student can see the assessments they received from their peers.
Recommendations for implementing workshop in the course
- Preliminary information is required - students will benefit more from this type of activity if they understand how the experience of assessment will benefit them.
Preparation should include a rationale for pedagogy, work instructions, a schedule, reference to the evaluation criteria, and training on how to give good feedback. - All of these may prevent resistance, reduce bias, and improve validity.
In addition, it is recommended to practice assessment, while presenting examples of good and bad evaluation.
- It is recommended to choose an exercise/task that has already been tested in previous semesters, and was found to be valid and reliable.
- In the preparation phase, defining the indicator is critical! The indicator (evaluation form) that includes criteria and performance levels, assists and guides students in providing an evaluation and grading. The quality of the indicator will affect the quality of the assessments (see Miller, 2003).
- Instruct students to justify/reason the decisions and grades, to prevent extraneous considerations in giving grades.
- It is recommended to publish the criteria at an early stage, so that they guide students starting from the preparation phase of the work.
- It is recommended to consider what the goal of integrating students in the evaluation is and, accordingly, what is the preferred way to assign work for evaluation, for example: defining groups of students (2-4), who will perform mutual evaluation.
- It is recommended to allow peer assessment and/or self-assessment as a bonus or permission rather than a requirement (see Komarov & Gajos, 2014).
- The Center for Promotion of Learning and Teaching offers pedagogical and technological support and friendly answers to questions. In addition, the Moodle Developers Forum offers support and answers to questions.
References
- Falchikov, N and Goldfinch, J. (2000). Comparing Peer and Teacher Marks Student Peer Assessment in Higher Education: A Meta-Analysis. Review of Educational Research. Vol 70 (3). pp287-322.
- Conway, R., Kember, D. Sivan, A. and Wu, M. (1993) Peer Assessment of an Individuals Contribution to a Group Project. Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education, 18 (1) 45-56.
- Komarov, S., Gajos , J. K. (2014). Organic Peer Assessment
- www.eecs.harvard.edu/~kgajos/papers/2014/komarov14organic.pdf
- Miller, P. J., (2003). “The Effect of Scoring Criteria Specificity on Peer and Self-Assessment”, Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, Volume 28, No 4, pp 383-394.
Written by Dr. Irit Wertheim
Step 1 - Creating the Workshop
This step is intended to determine the settings of the activity and is visible only to the editor (teacher).
A. Workshop Name – It is recommended to give a clear and concise name.
B. Grading settings – The grading settings will determine how the evaluation form will look, and how the final grade will be calculated for all its components, in a given assignment. Please note: The grading strategy cannot be changed after the assignment has been submitted.
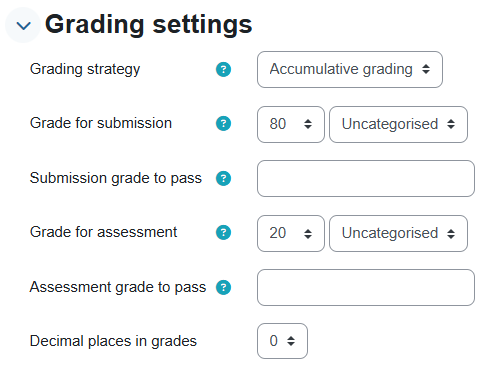
- Grading Strategy:
- Cumulative Grade - Comments and a grade are given in relation to the aspects specified
- Comments - Given in relation to the aspects specified, but no grade can be given
- Number of Errors - Comments and a True/False style assessment are given
- Rubric - Performance assessment is given, in relation to pre-determined criteria
- The student's grade in a workshop activity is the sum of:
- Submission Grade: A grade calculated based on the weighted average of the grades given during the peer assessment process.
- Evaluation score: A score is calculated automatically by checking the compatibility between the different assessments (of different participants). The calculation is done automatically.
Recommendation: Set the evaluation score and submission score to 100, and do the weighting in the general grade report.
Self-assessment can also be enabled.
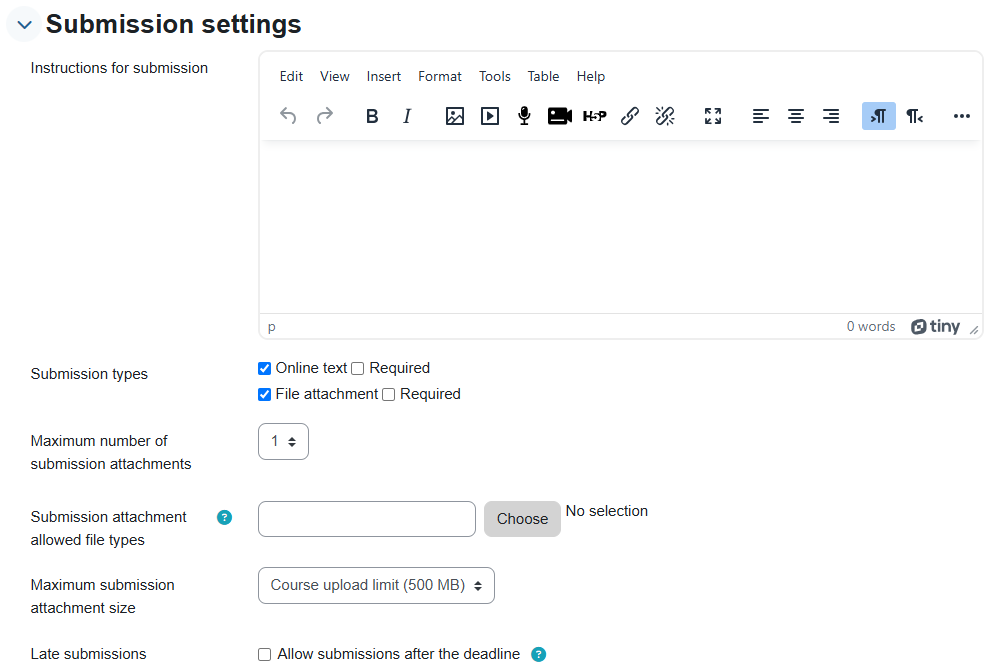
C. Display settings - What will be displayed to the participant when they are asked to submit the work: submission settings and later assessment settings.
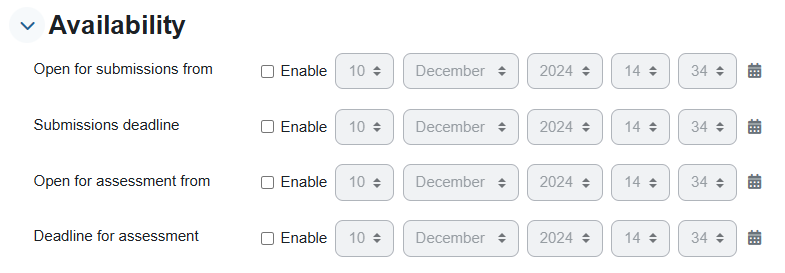
D. Availability: The time frame allocated for submission and evaluation
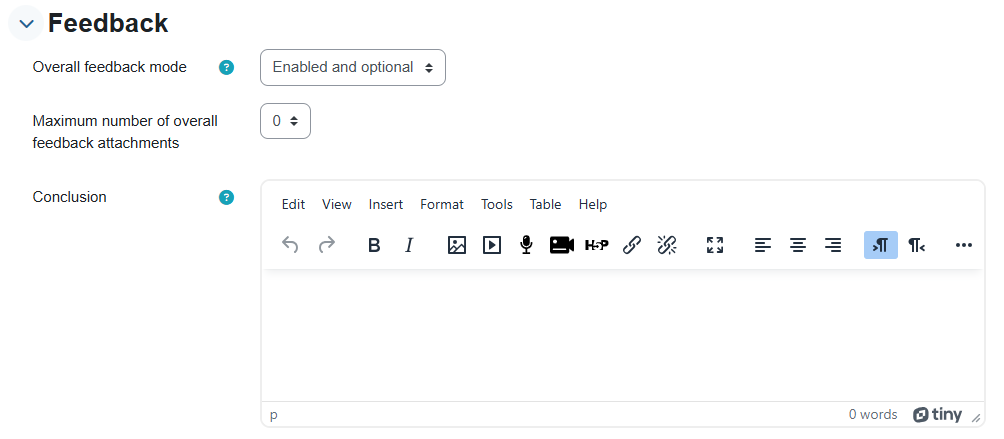
E. Conclusion: General feedback to be written by the lecturer (in the feedback options).
Step B - Using Workshop
Enter the Workshop task in the menu.
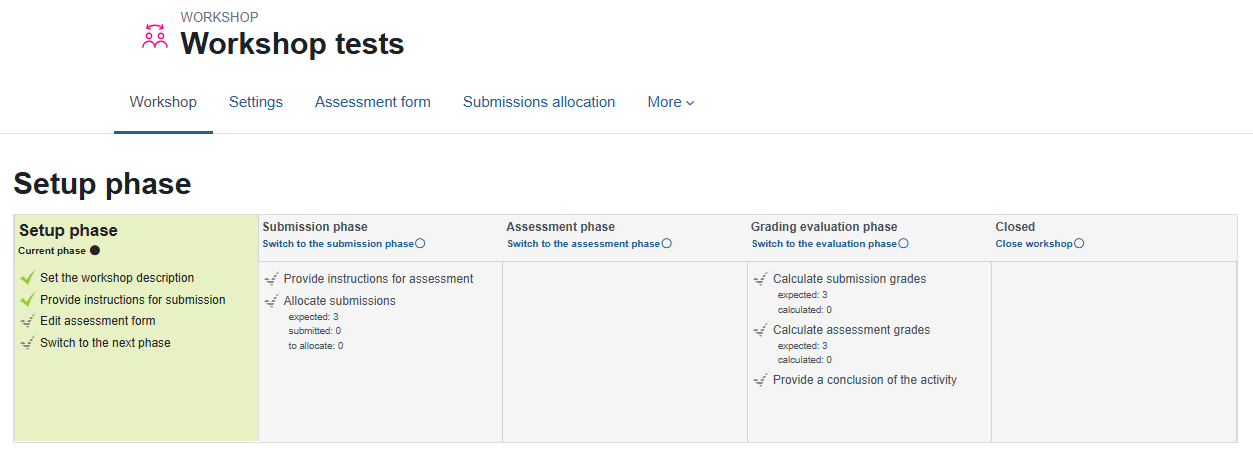
The workshop is organized in stages.
Next to each stage is a circle that is used to navigate between the different stages.
1. Aspect Definition Stage – The aspect is a set of criteria used by students in evaluating their peers’ work. Preparing the indicator requires thinking and planning, so it is recommended to prepare in advance.
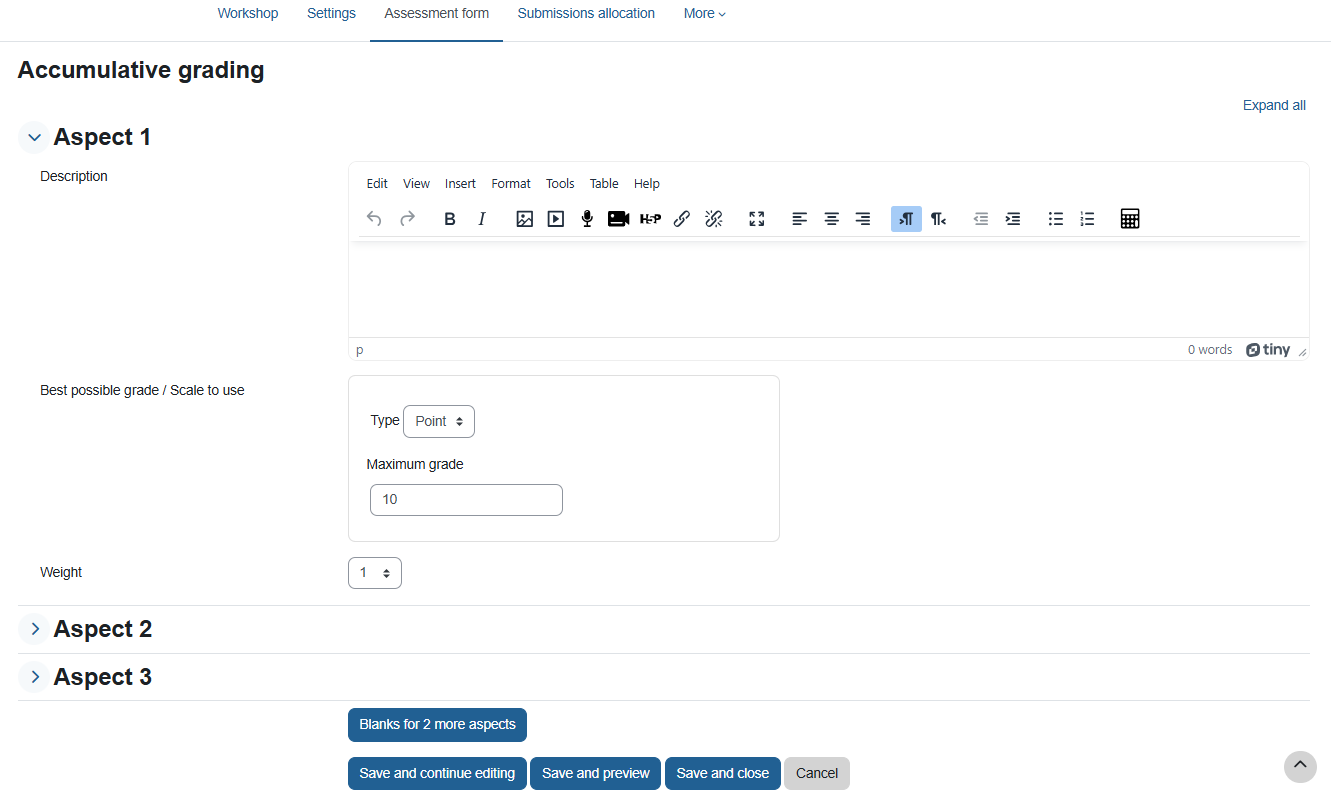
The teacher is required to set a maximum score and weight for each of the criteria (aspect).
The default is to set 3 criteria, but it is possible to add additional criteria.
The sum of all the scores given to the various criteria constitutes the full score for the assignment. The system will not allow you to advance to the next stage as long as the sum does not match the previous settings.
2. Submission Phase
At this stage, students upload their work and the work is assigned for review. This is a preliminary stage to the assessment phase, and assessment can only begin after the submission is complete.
It is recommended to upload examples of submissions in order to assist students and focus the assessment.
It is recommended to draw students' attention to the fact that this assignment allows only one submission!
A. Submissions - There is monitoring of the amount of work submitted so far and the amount of work expected to be received (depending on the number of students registered for the course).
After submission, the student who submitted receives a notification that the work has been received, and will later receive a notification by email when feedback on his work is submitted.
B. Assignment of submissions (for evaluation) - Distribution of the work for evaluation among the students. It is recommended that each student receive an odd number of work for evaluation.
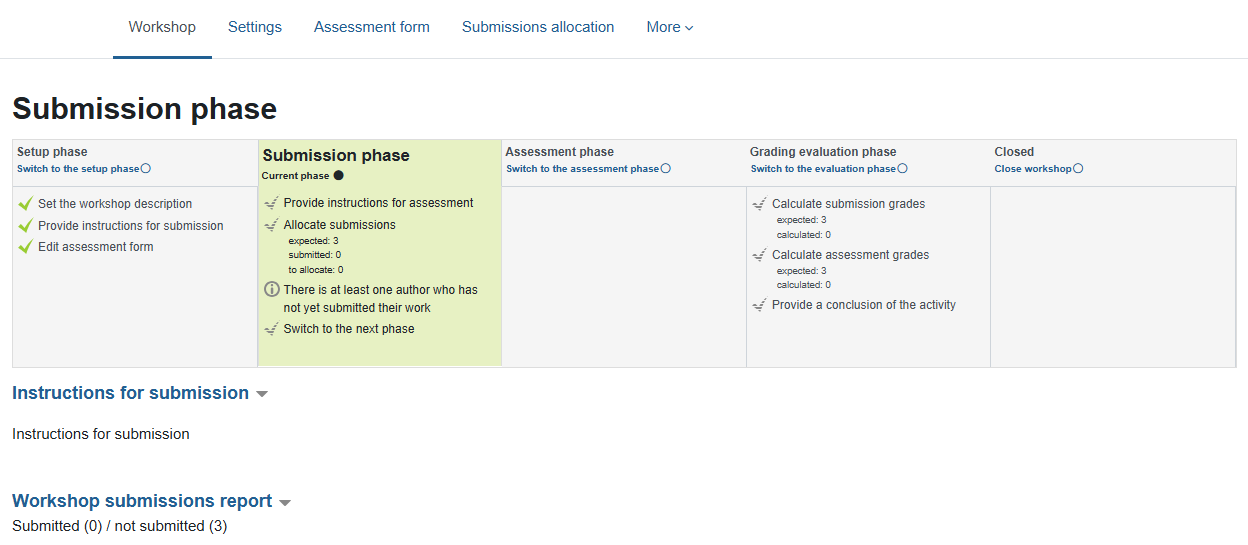
Clicking on "Allocate Submissions" will open the following screen:
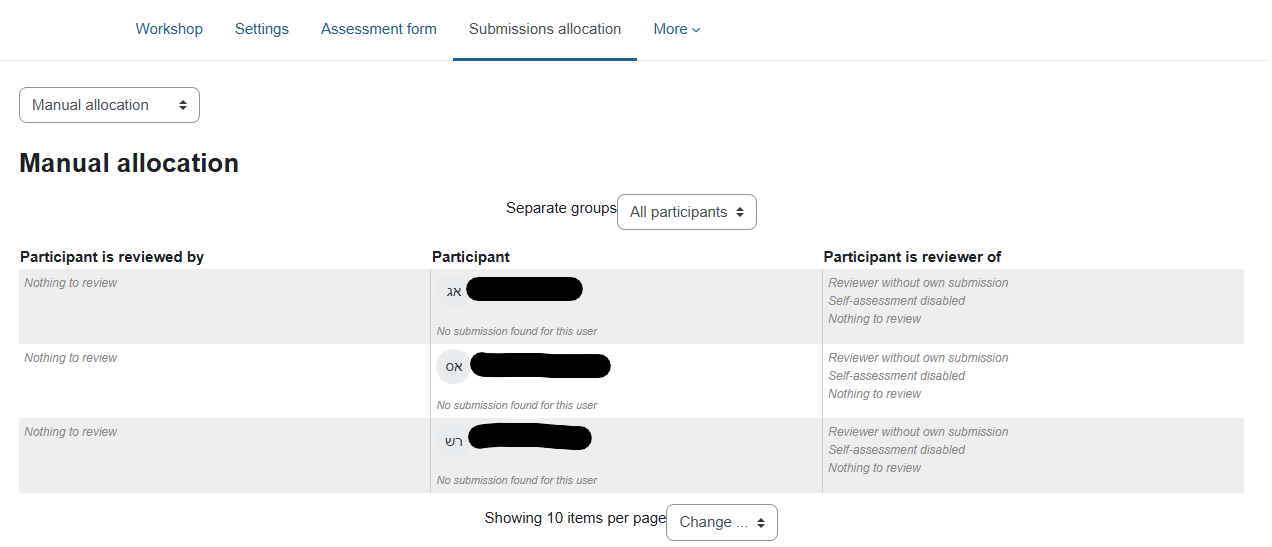
You can choose the assignment method: manual allocation (the teacher chooses for each student which assignments to evaluate), random allocation (you must choose how many students will evaluate each assignment and the system randomly distributes the assignments among the students) or scheduled allocation (identical to the random method and is also performed automatically at the end of the submission deadline).
When the allocation is complete, click on the assignment name (at the top of the page) to return to the assignment page.
Step 3. Assessment stage
At this stage, students assess their peers' assignments using the predefined evaluation form (assessment aspects).
For each assignment to be evaluated, the student must open the file and fill out feedback according to the grade scale set and add comments.
* The evaluating student can download the file to his or her computer, write comments, and send the file with the comments back to the student who submitted the assignment.
Please note! The default for peer review is that students can know who created the assignment they are reviewing. To perform the process anonymously, ask the IT team (Dr. Olga Chuntonov, olgac@tx.technion.ac.il or by phone 2726) to change the permissions.
Teachers can see a table summarizing the assignments that were uploaded, the feedback, and the grades given.
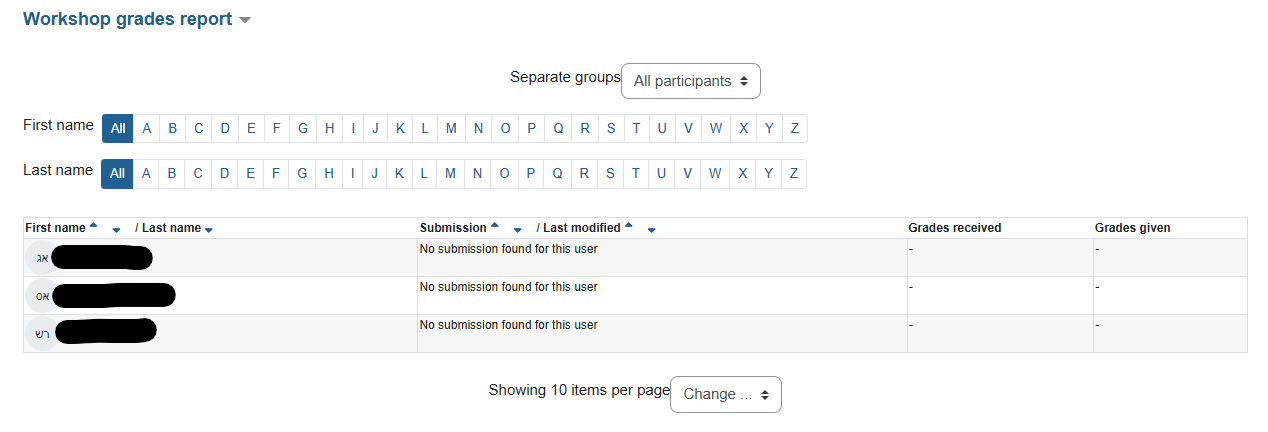
A teacher can change the weight that a particular assessment receives on the overall grade, or override the student's numerical assessment, assign a different grade or a verbal assessment. Unless otherwise specified, the grade will be determined as the average of the responses.
* In parentheses is a score for the evaluation given by the participant (the quality of the evaluation calculated by the system).
Step 4. Grading
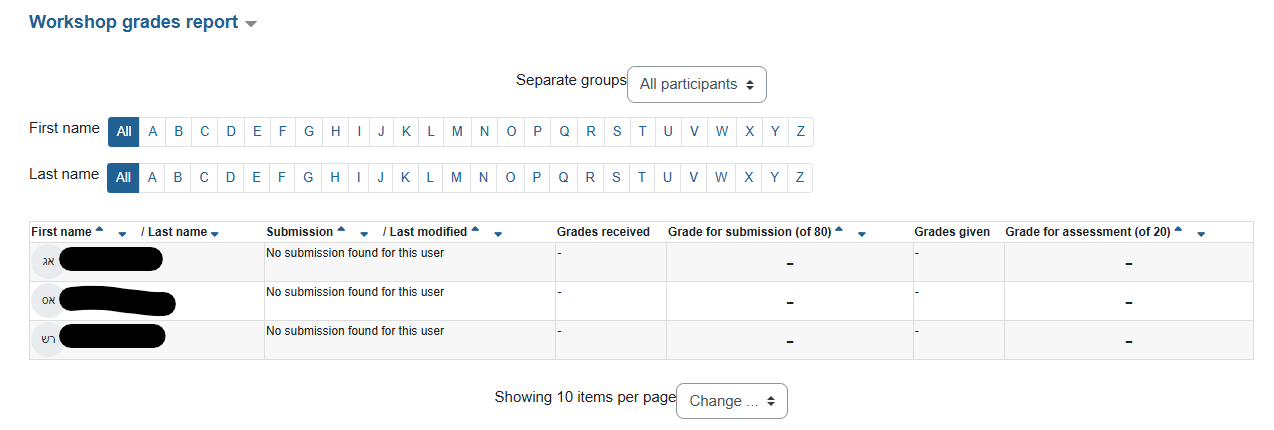
At this stage, the lecturer will see the summary of the students' activity (submission and assessment) and the grades will be updated automatically.
The system performs an automatic calculation to weight the assessments (default – average).
Each student receives two grades:
- Grade on their work (average)
- Grade on their assessment – quality of the assessment (appears in parentheses) proximity/deviation to the average
Step 5. Closing
After calculating all grades – a summary of the activity will be displayed, which will be prepared by the lecturer.
Links to additional tutorials
Written guides:
Workshop module (from Moodle)
Create a Workshop Activity in Moodle (from UNSW)
Workshop activity for peer assessment (from UCL)
Tutorial videos:
Using the 'Workshop' module for self and peer assessment in Moodle (iTeachWithMoodle)